Unity网络开发基础(一)
内容概况:TCP同步和异步通信,UDP同步和异步通信
一、网络通信
1.网络通信概述
(1)弱联网和强联网游戏
- 弱联网游戏:
这种游戏不会频繁的进行数据通信,客户端和服务端之间每次连接只处理一次请求,服务端处理完客户端的请求后,返回数据就断开连接。- 强联网游戏:
这种游戏会频繁的和服务端进行通信,会一直和服务段保持连接状态,不停的和服务器之间交换数据。
(2)长连接和短连接游戏
- 这是按照网络游戏通信特点划分的。
- 我们可以认为‘
- 弱联网游戏——>短连接游戏
- 强联网游戏——>长连接游戏
- 短连接游戏
需要传输数据时,建立连接,传输数据,获得响应,断开连接。- 通信特点:
需要通信时再连接,通信完毕就断开。- 通信方式:
HTTP超文本传输协议、HTTPS(它们本质上是TCP协议)
- 长连接游戏
- 不管是否需要传输数据,
客户端和服务器一直处于连接状态,除非一端主动断开,或者出现意外情况(客户端关闭或服务器崩溃)。- 通信特点:
连接一直建立,可以实时的传输数据。- 通信方式:TCP传输协议或UDP用户数据报协议
(3)Socket、HTTP、FTP
- Socket:
网络套接字,是对网络中不同主机上的应用程序之间进行双向通信的端点的抽象,一个套接字就是网络上进程通信的一段,提供了应用层进程利用网络协议交换数据的机制。- 主要用于制作长连接游戏
- Http/Https:
(安全的)超文本传输协议,是一个简单的请求-响应协议,它通常运行在TCP协议之上,它指定了客户端可能发送给服务端什么样的信息以及得到什么样的响应。主要制作短连接游戏,也可以用来进行资源下载
- FTP:
文件传输协议,是用于在网络上进行文件传输的一套标准协议。可以利用它来进行网络上资源的下载和上传。它也是基于TCP的传输,是面向连接的。
2.通信前的必备知识
(1)IP地址和端口类
① IP类和端口类用来干什么?
IP和端口号可以定位为网络中的设备C#中提供的对应的类 来声明对应的信息
② IPAddress类
- 命名空间:
- System.Net。
初始化IP信息的方式
- 用byte数组进行初始化(
不推荐)
2
IPAddress ip1 = new IPAddress(ipAddress);
用long长整型进行初始化(
不建议)
- 字符串转换(推荐)
特殊IP地址
127.0.0.1代表本机地址- 一些静态成员
- IPAddress.IPv6Any(获取可用的IPv6地址)
③ IPEndPoint类
IP地址和端口号的组合类初始化:
(2)域名解析
① 什么是域名解析?
- 将好记的
域名解析成IP- IP地址是网络上表示站点的数字地址,但是IP地址记忆困难。为了方便记忆,所以用域名代替IP
- 比如:一个网页www.baidu.com就是一个域名
- 域名解析解析就是
域名到IP地址的转换过程。域名的解析工作由DNS服务器完成域名系统(DNS)是互联网的一项服务,是一个将域名和IP地址映射的数据库
②IPHostEntry类
- 主要作用:域名解析后的返回值 可以通过该对象湖片区IP地址、主机名等待信息(
该类不会自己生命,都是作为某方法的返回值返回信息)
- 获取关联IP 成员变量:AddressList
- 获取主机别名列表 成员变量:Aliases
- 获取DNS名称 成员变量:HostName
③Dns类
主要作用:Dns是一个静态类,主要
根据域名获取IP地址常用方法:
- 获取
本地系统的主机名
- 获取指定域名的IP信息
同步获取:
注意:由于获取远裁主机信息是需要进行网络通信,可能会堵塞主线程
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
for (int i = 0; i < entry.AddressList.Length; i++)
{
print("IP地址" + entry.AddressList[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < entry.Aliases.Length; i++)
{
print("主机别名" + entry.Aliases[i]);
}
print("DNS名字" + entry.HostName);
异步获取:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
private async void GetHostEntry()
{
Task<IPHostEntry> task = Dns.GetHostEntryAsync("www.baidu.com");
await task;
for (int i = 0; i < task.Result.AddressList.Length; i++)
{
print("IP地址" + task.Result.AddressList[i]);
}
for (int i = 0; i < task.Result.Aliases.Length; i++)
{
print("主机别名" + task.Result.Aliases[i]);
}
print("DNS名字" + task.Result.HostName);
}
(3)序列化和反序列化2进制数据
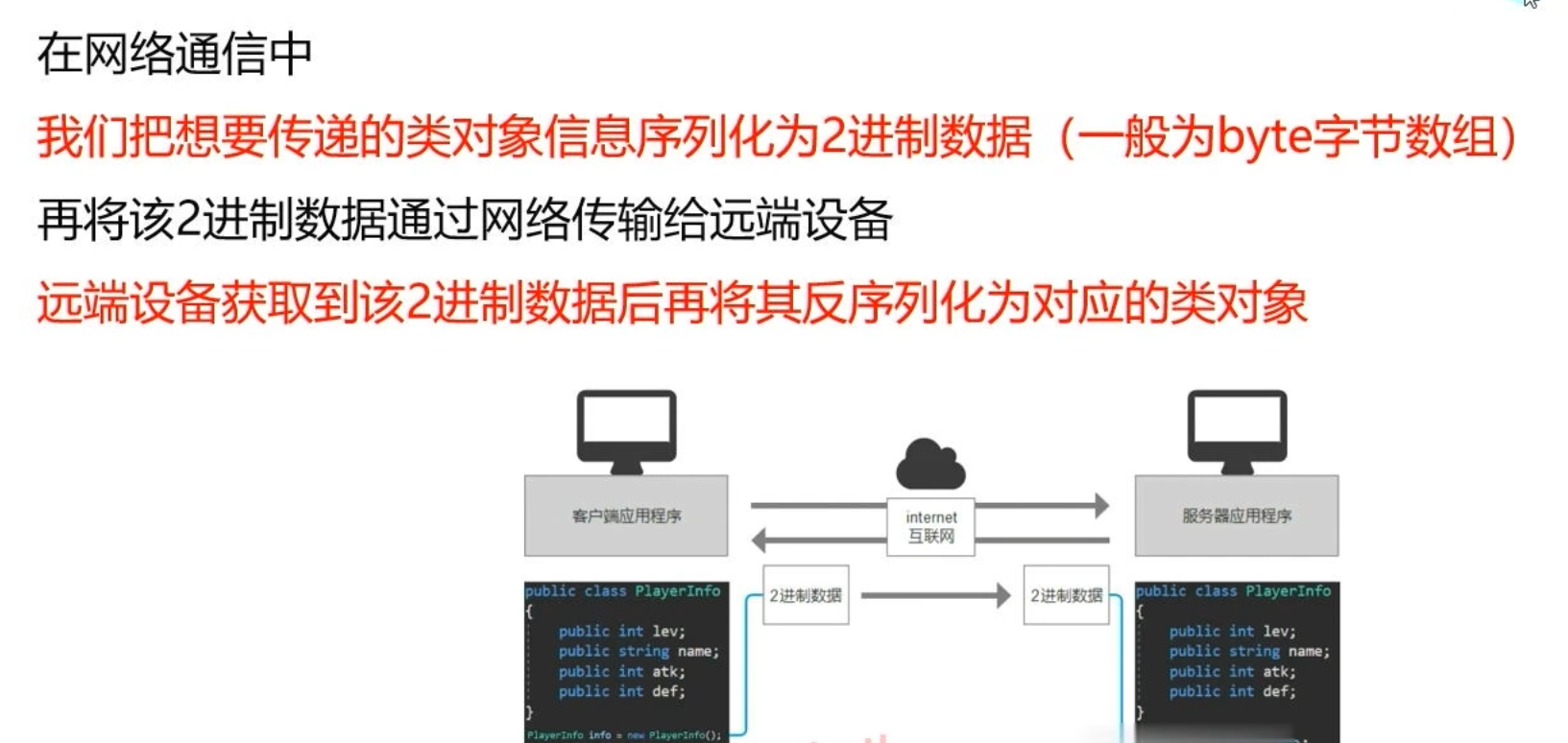



① 序列化
非字符串类型转字节数组
关键类:
BitConverter主要作用:
除了字符串的其他常用类型和字节数组相互转换
字符串类型转字节数组
关键类:
Encoding主要作用:将字符串类型和字节数组相互转换,并且决定转换时使用的字符编码类型。(
网络通信时建议大家使用UTF-8类型)。
如何将一
个类对象转换为二进制???
注:网络通信中我们是不能使用二进制知识点中BinaryFormatter 2进制格式化类具体步骤:
明确字节数组的容量(
注意:在确定字符串字节长度时,要考虑解析时如何处理)(先存字符串长度,再存字符串2进制数组)申明一个装在信息的字节数组容器
将对象中的所有信息转为字节数组并放入该容器中(
可以利用数组中的CopeTo方法转存字节数组)CopyTo方法的第二个参数代表 从容器的第几个位置开始存储。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
info.lev = 10;
info.name = "wqx";
info.atk = 100;
info.sex = false;
//字节数组需要的容量
int indexNum = sizeof(int) +
sizeof(int) +//表示name字符串转换成字节数组后 数组的长度
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(info.name).Length +//字符串具体字节数组的长度
sizeof(short) +
sizeof(bool);
//申明一个装载信息的字节数组容器
byte[] playerBytes = new byte[indexNum];
//将对象中的所有信息转为字节数组并放入该容器中(`可以利用数组中的CopeTo方法转存字节数组`)
// CopyTo方法的第二个参数代表 从容器的第几个位置开始存储
int index = 0;
BitConverter.GetBytes(info.lev).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
//姓名
byte[] strBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(info.name);
int num = strBytes.Length;
//存储的是字符串数组长度
BitConverter.GetBytes(num).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
//存储的是字符串的字节长度
strBytes.CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += num;
//攻击
BitConverter.GetBytes(info.atk).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(short);
//性别
BitConverter.GetBytes(info.sex).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(bool);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
{
public int lev;
public string name;
public short atk;
public bool sex;
public byte[] GetBytes()
{
int indexNum = sizeof(int) +
sizeof(int) +//表示name字符串转换成字节数组后 数组的长度
Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(info.name).Length + //字符串具体字节数组的长度
sizeof(short) +
sizeof(bool);
//申明一个装载信息的字节数组容器
byte[] playerBytes = new byte[indexNum];
//将对象中的所有信息转为字节数组并放入该容器中(`可以利用数组中的CopeTo方法转存字节数组`)
// CopyTo方法的第二个参数代表 从容器的第几个位置开始存储
int index = 0;
BitConverter.GetBytes(lev).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
//姓名
byte[] strBytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes(name);
int num = strBytes.Length;
//存储的是字符串数组长度
BitConverter.GetBytes(num).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(int);
//存储的是字符串的字节长度
strBytes.CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += num;
//攻击
BitConverter.GetBytes(.atk).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(short);
//性别
BitConverter.GetBytes(sex).CopyTo(playerBytes, index);
index += sizeof(bool);
return playerBytes;
}
}
② 反序列化
字节数组转
非字符串关键类:
BitConverter
2
int i = BItConverter.ToInt32(bytes,0);
- 字节数组转字符串
- 关键类:Encoding
- 命名空间:System.Text
2
string str = Encoding.UTF8.GetString(bytes2,0,bytes2.Length);
- 如何将2进制数据转为一个类对象
- 获取对应的字节数组
- 将字节数组按序列化的顺序进行反序列化(将对应字节分组转换为对应类型变量)
3. 套接字Socket
(1)Socket重要API
① Socket套接字的作用
类名:Socket
命名空间:System.Net.Sockets
Socket套接字是支持
TCP/IP网络通信的基本操作单位一个套接字包括以下关键信息:
本机的IP地址和端口
对方的IP地址和端口
- 双方的通信协议
一个Socket对象表示一个本地或者远程套接字信息
- 它被视为一个
数据通道- 这个通道连接客户端和服务端
- 数据的发送和接收在这个通道进行
一般制作长连接游戏时,我们会使用Socket套接字作为我们的通信方案
② Socket的类型
一共由
三种类型
流套接字
- 主要用于实现
TCP通信,提供面向连接、可靠的、有序的、数据无差错且无重复的数据传输服务。
数据报套接字
- 主要用于实现
UDP通信,提供了无连接的通信服务,数据包的长度不能大于32KB- 不提供正确性检查,不保证顺序,可能出现重发,丢失等情况
- 原始套接字(不常用,不细讲)
- 主要用于实现IP数据包通信,用于之间访问协议的较低层,常用于侦听和分析数据包。
③ Socket构造函数

- 通过Socket构造函数,我们可以申明不同类型的套接字
参数一:
AddressFamily网络寻址枚举类型,决定寻址方案
常用 InterNetworkIPv4寻址 InterNetwork6IPv6寻址 做了解 UNIX UNIX本地到主机地址 ImpLink ARPANETIMP地址 Ipx Ipx或SPX地址 Iso ISO协议地址 Osi OSI协议地址 NetBios NetBIOS地址 Atm 本机ATM服务地址 参数二 :SocketType 套接字枚举类型,决定使用的套接字类型
常用 Dgram支持数据报、最大长度固定的无连接、不可靠的消息( 主要用于UDP通信)Stream支持可靠、双向、基于连接的字节流( 主要用于TCP通信)做了解 Raw 支持对基础传输协议的访问 Rdm 支持无连接、面向消息、以可靠方式发送的消息 Seqpacket 提供排序字节流的面向连接且可靠的双向传输 参数三:ProtocolType 协议类型枚举类型,决定套接字使用的通信协议
TCP TCP传输控制协议 UDP UDP用户数据报协议 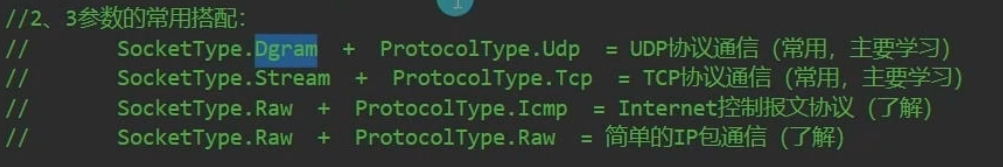
2
3
4
5
Socket socketTcp = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
//UDP数据报套接字
Socket socketUdp = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Dgram, ProtocolType.Udp);
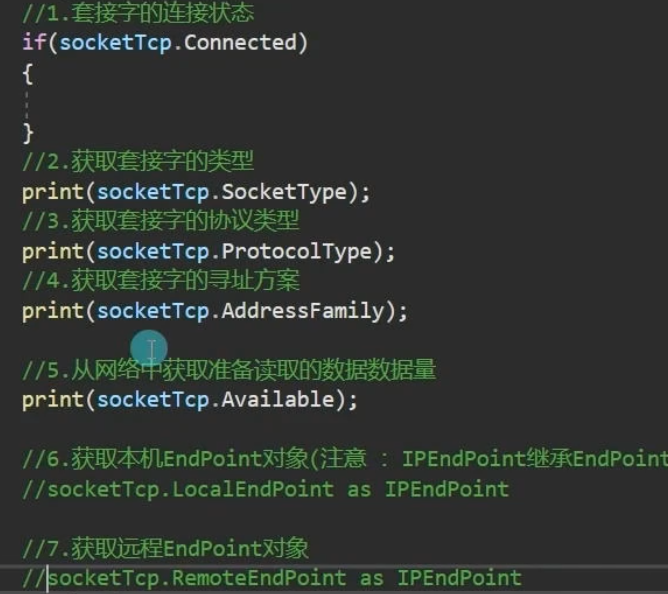
④ Socket的常用属性
⑤ Socket的常用方法
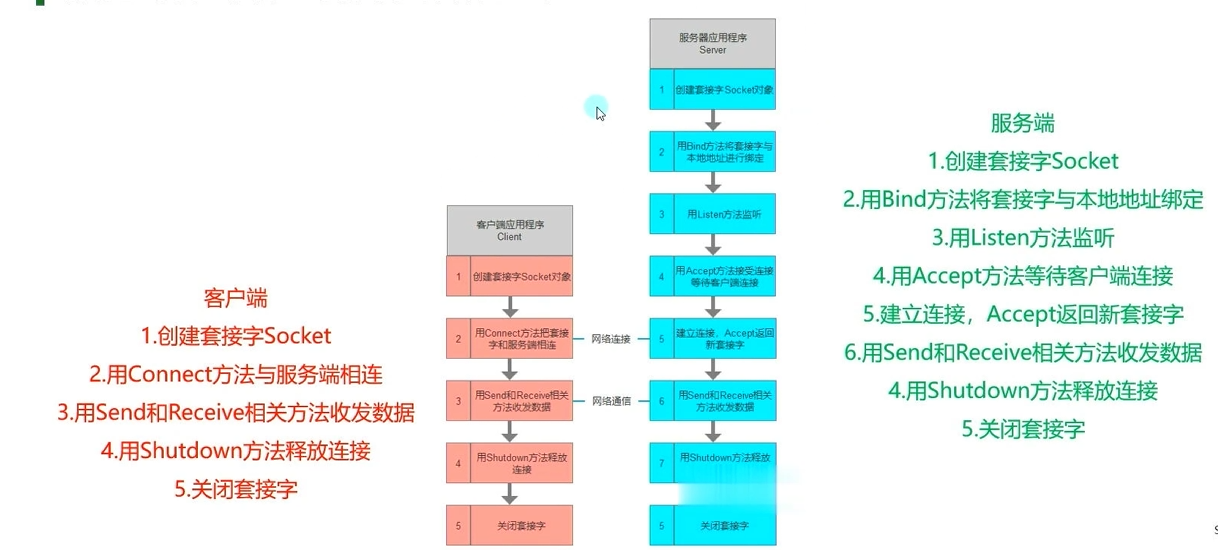
(2)Socket套接字TCP通信
① 概述
- 服务端和客户端需要做什么???
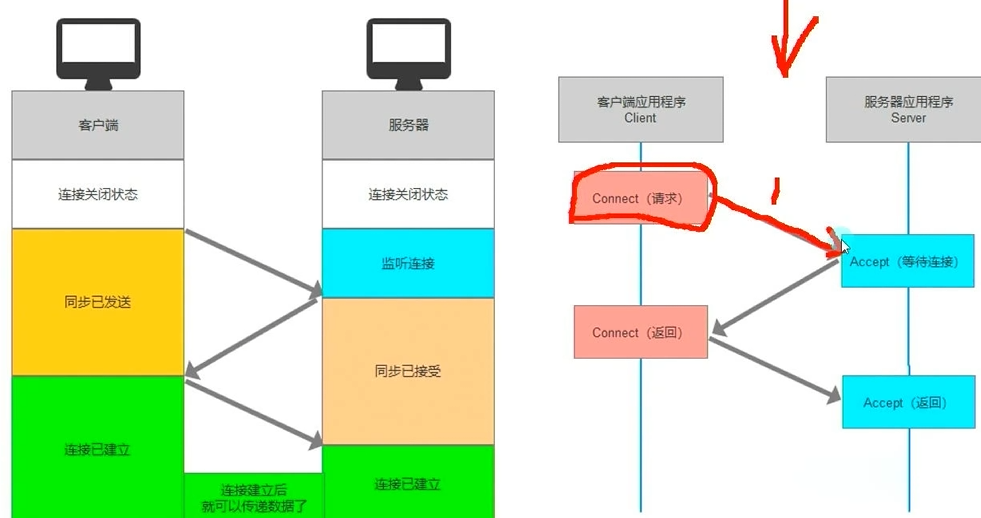
- TCP协议三次握手的体现
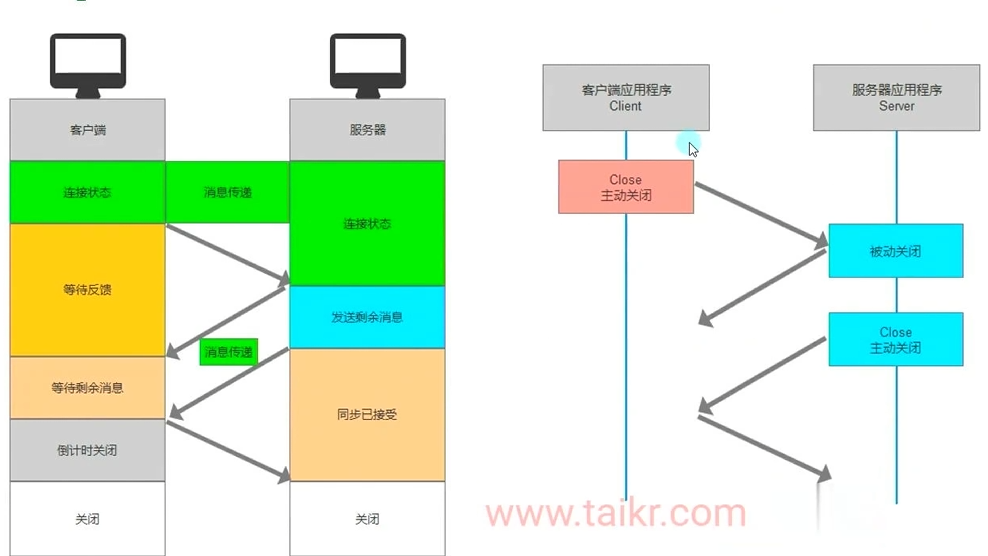
- TCP协议四次挥手的体现
4.TCP通信
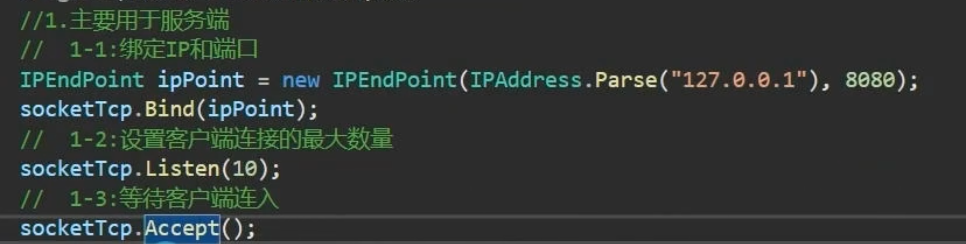
(1)服务端(同步)
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
Socket socketTcp = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
//2.Bind方法将套接字于本地地址绑定
try
{
IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1"), 8080);//端口号要大于1024且不能被别的应用程序占用
socketTcp.Bind(ipPoint);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("绑定错误" + e.Message);
return;
}
//3. 用Listen方法监听
socketTcp.Listen(1024);//最多1024台设备连接进来
Console.WriteLine("服务端绑定监听结束,等待客户端连入");
//4. 用Accept方法等待客户端连接, 5.建立连接后返回新的套接字
Socket socketClient = socketTcp.Accept();
Console.WriteLine("{0}连接成功", socketClient.RemoteEndPoint.ToString());
//6.用Send和Receive方法收发数据
//发送
socketClient.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("欢迎连入客户端"));
//接收
byte[] result = new byte[1024]; //缓存数组
int receiveNum = socketClient.Receive(result);
Console.WriteLine("接收到了{0}发来的消息:{1}",
socketClient.RemoteEndPoint.ToString(), Encoding.UTF8.GetString(result, 0, receiveNum));
//7.用Shutdown方法释放连接
socketClient.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
//8.关闭套接字
socketClient.Close();
Console.WriteLine("按任意键退出");
Console.ReadKey();
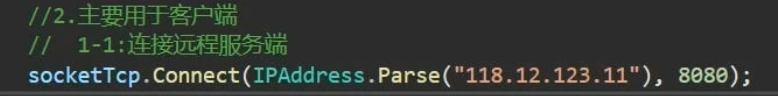
(2)客户端(同步)

2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
Socket socketTcp = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Stream, ProtocolType.Tcp);
//2.用Connect方法于服务端相连
try
{
IPEndPoint ip = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1"), 8080);//填远端服务器和端口号
socketTcp.Connect(ip);
}
catch (SocketException e)
{
if (e.ErrorCode == 10061)
{
print("服务器拒绝连接");
}
else
{
print("服务器连接失败" + e.Message);
}
}
//3.用send和receive收发数据
//接收数据
byte[] receiveBytes = new byte[1024];
int receiveNum = socketTcp.Receive(receiveBytes);
print("收到服务端发来的消息:" + Encoding.UTF8.GetString(receiveBytes, 0, receiveNum));
//发数据
socketTcp.Send(Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("我是姚兆龙"));
//4.Shutdown 释放连接
socketTcp.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
//5.关闭套接字
socketTcp.Close();

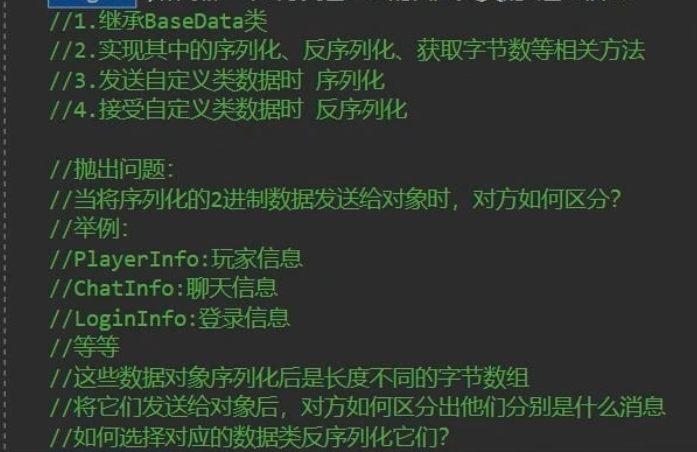
(3)区分消息类型
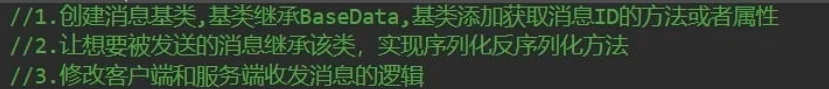
① 如何发送之前自定义类的2进制信息
② 如何区分消息
解决方案:
- 为发送的信息添加标识,比如
添加消息ID- 再所有发送的消息的头部上添加消息ID(int,short,byte都可以)
③ 实践
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
{
public override int GetBytesNum()
{
throw new System.NotImplementedException();
}
public override int Reading(byte[] bytes, int beginIndex = 0)
{
throw new System.NotImplementedException();
}
public override byte[] Writing()
{
throw new System.NotImplementedException();
}
public virtual int GetID()
{
return 0;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
{
/// <summary>
/// 玩家ID
/// </summary>
public int playerID;
public PlayerData playerData;
public override int Reading(byte[] bytes, int beginIndex = 0)
{
//反序列化不需要解析id,在这之前就该把ID反序列化出来
//用来判断到底使用哪一个自定义类来反序列化
int index = beginIndex;
playerID = ReadInt(bytes, ref index);
playerData = ReadData<PlayerData>(bytes, ref index);
return index - beginIndex;
}
public override byte[] Writing()
{
int index = 0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[GetBytesNum()];
//写入消息id
WriteInt(bytes, GetID(), ref index);
//消息成员变量
WriteInt(bytes, playerID, ref index);
WriteData(bytes, playerData, ref index);
return bytes;
}
/// <summary>
/// 自定义消息ID 主要用于区分哪一个消息
/// </summary>
/// <returns></returns>
public override int GetID()
{
return 1001;
}
public override int GetBytesNum()
{
//消息id+玩家id+玩家数据类
return 4 + 4 + playerData.GetBytesNum();
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
int receiveNum = socketTcp.Receive(receiveBytes);
//首先解析消息ID
int msgID = BitConverter.ToInt32(receiveBytes, 0);
switch (msgID)
{
case 1001:
PlayerMsg msg = new PlayerMsg();
msg.Reading(receiveBytes, 4);
print(msg.playerID);
print(msg.playerData.name);
break;
}
坑:
对于数据结构类不要继承MonoBehaviour,如果继承了强行new ,得到的结果为null。
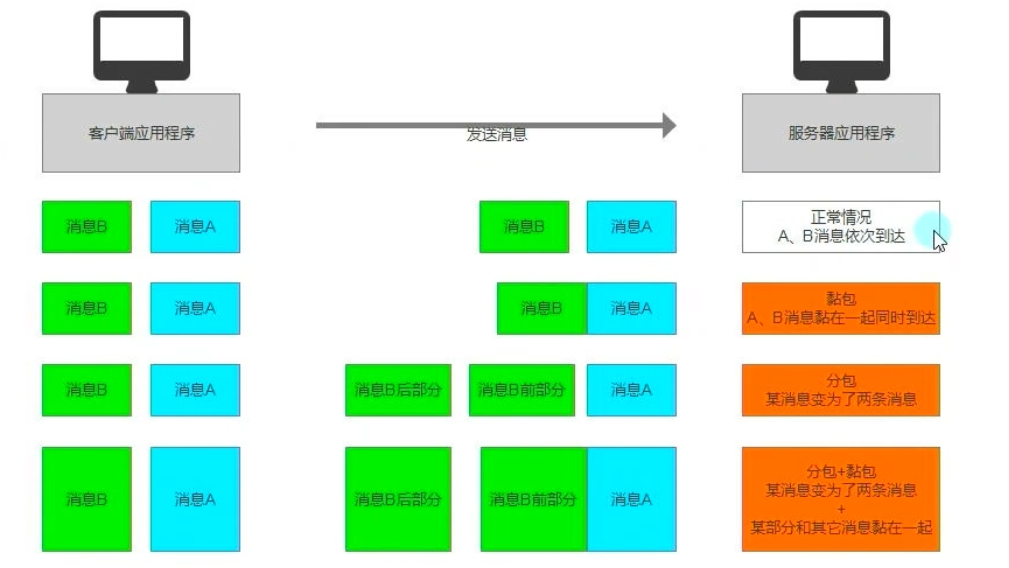
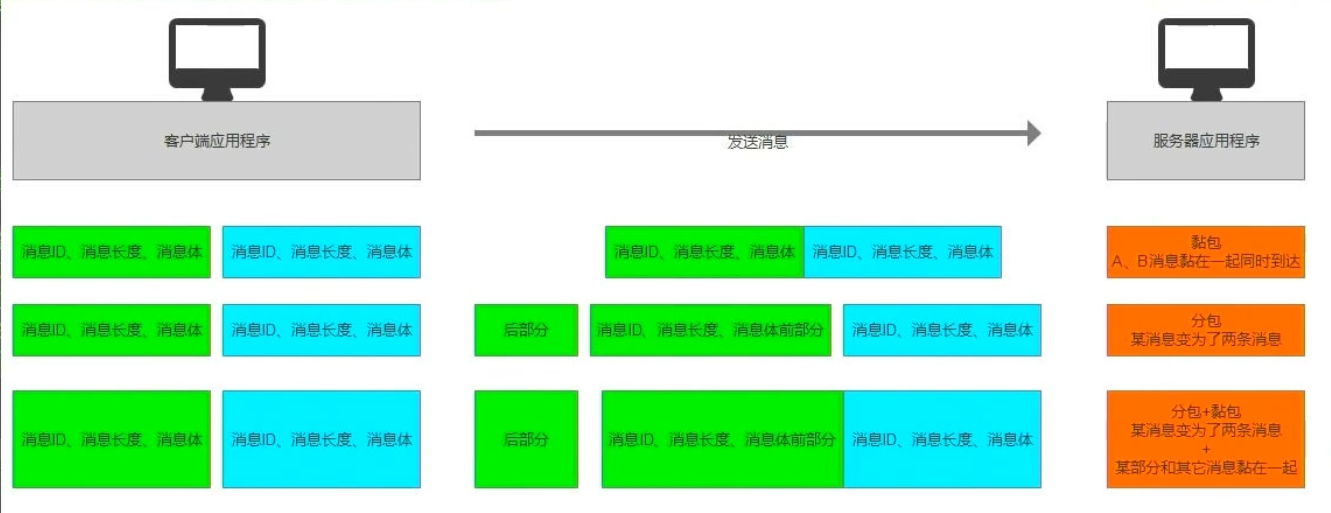
(4)分包和黏包
- 分包和黏包指再网络通信中由于各种因素(网络环境或API规则)造成的消息和消息之间出现的两种状态。
分包:一个消息分成了多个消息发送黏包:一个消息和另外一个消息黏在了一起。- 注:分包和黏包可能同时发生
- 解决分包和黏包
- 突破点:
- 在头部添加一个消息长度。当我们接收信息时通过消息长度来判断是否发送分包和黏包。
- 再对消息进行拆分处理、合并处理。我们每次只处理完整的信息。
- 实践解决
- 为所有消息添加头部信息,用于存储消息长度
- 根据分包、黏包的表现情况,修改接收消息处的逻辑
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
/// 处理分包黏包问题的方法
/// </summary>
/// <param name="receiveBytes">缓存字节数组</param>
/// <param name="receiveNum">接收到的消息大小</param>
private void HandleReceiveMsg(byte[] receiveBytes, int receiveNum)
{
int msgID = 0;
int msgLength = 0;
int nowIndex = 0;
//收到消息之前 看看有没有缓存,有就拼接到后面
receiveBytes.CopyTo(cacheBytes, cacheNum);
cacheNum += receiveNum;
while (true)
{
//每一次将长度设置为-1 避免上一次解析的数据 影响这一次的判断
msgLength = -1;
//处理一条消息
if (cacheNum - nowIndex >= 8)
{
//解析消息ID
msgID = BitConverter.ToInt32(cacheBytes, nowIndex);
nowIndex += 4;
//解析消息体长度
msgLength = BitConverter.ToInt32(cacheBytes, nowIndex);
nowIndex += 4;
}
if (cacheNum - nowIndex >= msgLength && msgLength != -1)
{
//解析消息体
BaseMsg baseMsg = null;
switch (msgID)
{
case 1001:
PlayerMsg msg = new PlayerMsg();
msg.Reading(cacheBytes, nowIndex);
baseMsg = msg;
break;
}
if (baseMsg != null)
receiveQueue.Enqueue(baseMsg);
nowIndex += msgLength;
if (nowIndex == cacheNum)
{//解析完毕
cacheNum = 0;
break;
}
}
else
{
//如果不满足证明有分包
//我们要把当前收到的内容保存下来
//下次收到信息后,再处理
//receiveBytes.CopyTo(cacheBytes, 0);
//cacheNum = receiveNum;
//如果进行 id长度和长度解析 但是没有成功解析消息 我们需要减去nowindex移动的位置
if (msgLength != -1)
{
nowIndex -= 8;
}
Array.Copy(cacheBytes, nowIndex, cacheBytes, 0, cacheNum - nowIndex);
cacheNum = cacheNum - nowIndex;
break;
}
}
}
测试代码
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
{
btn.onClick.AddListener(() =>
{
PlayerMsg ms = new PlayerMsg();
ms.playerID = 1111;
ms.playerData = new PlayerData();
ms.playerData.atk = 1000;
ms.playerData.name = "wqx1";
ms.playerData.lev = 100;
NetMgr.Instance.Send(ms);
});
//黏包
btn1.onClick.AddListener(() =>
{
PlayerMsg ms = new PlayerMsg();
ms.playerID = 1111;
ms.playerData = new PlayerData();
ms.playerData.atk = 1000;
ms.playerData.name = "wqx2";
ms.playerData.lev = 100;
PlayerMsg ms1 = new PlayerMsg();
ms1.playerID = 100;
ms1.playerData = new PlayerData();
ms1.playerData.atk = 10;
ms1.playerData.name = "wqx3";
ms1.playerData.lev = 1;
byte[] bytes = new byte[ms.GetBytesNum() + ms1.GetBytesNum()];
ms.Writing().CopyTo(bytes, 0);
ms1.Writing().CopyTo(bytes, ms.GetBytesNum());
NetMgr.Instance.SendTest(bytes);
});
btn2.onClick.AddListener(async () =>
{
PlayerMsg ms2 = new PlayerMsg();
ms2.playerID = 100;
ms2.playerData = new PlayerData();
ms2.playerData.atk = 10;
ms2.playerData.name = "wqx4";
ms2.playerData.lev = 1;
byte[] bytes = ms2.Writing();
//分包
byte[] byte1 = new byte[10];
byte[] byte2 = new byte[bytes.Length - 10];
//分成第一个包
Array.Copy(bytes, 0, byte1, 0, 10);
Array.Copy(bytes, 10, byte2, 0, bytes.Length - 10);
NetMgr.Instance.SendTest(byte1);
await Task.Delay(500);
NetMgr.Instance.SendTest(byte2);
});
//分包+黏包
btn3.onClick.AddListener(async () =>
{
PlayerMsg ms = new PlayerMsg();
ms.playerID = 1111;
ms.playerData = new PlayerData();
ms.playerData.atk = 1000;
ms.playerData.name = "wqx2";
ms.playerData.lev = 100;
PlayerMsg ms1 = new PlayerMsg();
ms1.playerID = 100;
ms1.playerData = new PlayerData();
ms1.playerData.atk = 10;
ms1.playerData.name = "wqx3";
ms1.playerData.lev = 1;
byte[] bytes1 = ms.Writing();
byte[] bytes2 = ms1.Writing();
byte[] byte2_1 = new byte[10];
byte[] byte2_2 = new byte[bytes2.Length - 10];
Array.Copy(bytes2, 0, byte2_1, 0, 10);
Array.Copy(bytes2, 10, byte2_2, 0, bytes2.Length - 10);
//消息A和消息B前一段的黏包
byte[] bytes = new byte[bytes1.Length + byte2_1.Length];
bytes1.CopyTo(bytes, 0);
byte2_1.CopyTo(bytes, bytes1.Length);
NetMgr.Instance.SendTest(bytes);
await Task.Delay(2000);
NetMgr.Instance.SendTest(byte2_2);
});
}
(5)客户端主动断开连接
目前的客户端主动断开连接:
- 我们断开连接时调用的是socket 的 ShutDown和Close方法
- 但是通过调用这两个方法 后,服务端并不知道客户端已经主动断开
- Connected只能得到上一次收发消息是否成功
解决方法:
- 客户端尝试使用Disconnect方法主动断开连接(实测不行)
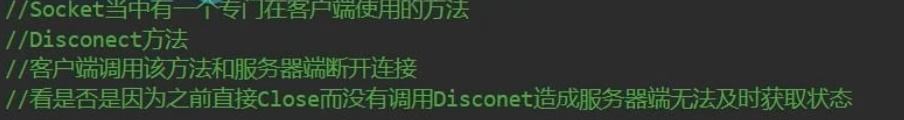
主要修改的逻辑:
客户端:主动断开连接
服务端:收发消息时判断socket是否已经断开,处理删除记录的socket相关逻辑(会用到线程锁)
- 自定义退出消息
- 让服务器端收到该消息就知道是客户端想要主动断开
- 然后服务器端处理是否socket相关工作
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
{
//
public override int GetID()
{
return 1003;
}
public override int GetBytesNum()
{
return 4 + 4;//消息ID+消息体长度 长度为0
}
public override byte[] Writing()
{
int index = 0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[GetBytesNum()];
WriteInt(bytes, GetID(), ref index);
WriteInt(bytes, 0, ref index);
return bytes;
}
public override int Reading(byte[] bytes, int beginIndex = 0)
{
return 0;
}
}
思路主要是:收到1003数据之后,把该socket添加到待移除列表,等服务器接收函数遍历字典完成后,
再遍历代移除列表,判断socket中有没有待移除的socket,有就按照socketID(键)移除。
(6)心跳消息
什么是心跳消息???* 所谓心跳信息,就是在长连接中,客户端和服务端之间`定期发送的一种特殊的数据包` * 用于通知对方自己还在线,以确保长连接的有效性。
* 由于其发送的时间间隔往往是固定的持续的,就像是心跳一样。
- 为什么需要心跳消息??
避免非正常关闭客户端时,服务器无法正常收到关闭连接消息
通过心跳消息我们可以自定义判断超时 ,如果超时没有收到客户端消息,证明客户端已经断开连接。
- 避免客户端长期不发送消息,防火墙或路由器会断开连接,我们可以通过心跳消息一直保持活跃。
- 实现心跳消息
客户端:
- 主要功能:定时发送消息
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
/// 发送心跳消息的间隔时间
/// </summary>
private int SEND_HEART_MSG_TIME = 2;
/// <summary>
/// 心跳消息对象
/// </summary>
private HeartMsg heartMsg = new HeartMsg();
InvokeRepeating("SendHeartMsg", 0, SEND_HEART_MSG_TIME);
public void SendHeartMsg()
{
if (isConnect)
{
Send(heartMsg);
}
}服务器:
- 主要功能:不停检测是上次收到某客户端消息的时间,如果超时则认为连接已经断开。
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
/// 上一次收到心跳信息的时间
/// </summary>
private long frontTime = -1;
/// <summary>
/// 心跳消息时间间隔
/// </summary>
private static int TIME_OUT_TIME = 10;
/// <summary>
/// 检测心跳消息超时 超时就断开
/// </summary>
private void ChechTimeOut(object obj)
{
while (Connected)
{
if (frontTime != -1 && DateTime.Now.Ticks / TimeSpan.TicksPerSecond - frontTime >= TIME_OUT_TIME)
{
Program.socket.AddDelSocket(this);
break;
}
Thread.Sleep(5000);
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
public class HeartMsg : BaseMsg
{
public override int GetID()
{
return 999;
}
public override int GetBytesNum()
{
return 4 + 4;//消息ID+消息体长度 长度为0
}
public override byte[] Writing()
{
int index = 0;
byte[] bytes = new byte[GetBytesNum()];
WriteInt(bytes, GetID(), ref index);
WriteInt(bytes, 0, ref index);
return bytes;
}
public override int Reading(byte[] bytes, int beginIndex = 0)
{
return 0;
}
}
(7)异步通信
异步方法和同步方法的区别
- 同步方法:
- 方法中逻辑执行
完毕后,再继续执行后面的方法。- 异步方法:
- 方法中的逻辑还没有执行完,就继续执行后面的逻辑。
- 异步方法的
本质:
- 往往异步方法当中都会使用多线程执行某部分逻辑
- 因为我们不需要等待方法中逻辑执行完毕,就可以继续执行下面的逻辑了。
注意:
- Unity中协同程序中的某些异步方法,有的使用的是多线程,有的使用的是迭代器分布进行。
举例说明异步方法原理
异步倒计时为例
线程回调
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
{
Thread t = new Thread(() =>
{
while (true)
{
print("倒计时:" + second);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
second--;
if (second == 0)
break;
}
callBack?.Invoke();
});
t.Start();
print("开启倒计时");
}
2. async和await 会等待线程执行完毕 继续执行后面的逻辑(相对第一种,可以让函数分布执行)
```C
public async void CountDownAsync(int second)
{
print("倒计时开始");
await Task.Run(() =>
{
while (true)
{
print("倒计时:" + second);
Thread.Sleep(1000);
second--;
if (second == 0)
break;
}
});
print("倒计时结束");
}
① Socket TCP通信中的 异步方法(Begin开头方法)
- 回调函数参数
IAsyncResult
AsyncState调用异步方法时传入的参数 需要转换AsyncWaitHandle用于同步等待
服务器相关 异步方法
BeginAccept
- 第一个参数:回调函数
- 第二个参数:传入当前socket,在内部可以通过回调函数参数的形式获取
EndAccept
客户端:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1"), 8080);
socketTcp.BeginConnect(ipPoint, (result) =>
{
try
{
socketTcp.EndConnect(result);
print("连接成功");
}
catch (SocketException e)
{
print("连接出错" + e.Message);
}
}, socketTcp);服务器:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
socketTcp.BeginAccept((result) =>
{
try
{
//获取传入的参数;就是外部的socketTcp
Socket s = result.AsyncState as Socket;
//通过调用EndAccept就可以获取连入的客户端socket
Socket clientSocket = s.EndAccept(result);
}
catch (SocketException e)
{
print(e.SocketErrorCode);
}
}, socketTcp);
接收消息(服务器客户端通用)BeginReceive(用于接收的字节数组,数组开始接收的位置,接收长度,标识,回调函数,当前socket)
EndReceive
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
socketTcp.BeginReceive(ipPoint, ReceiveCallBack, socketTcp);
private void ReceiveCallBack(IAsyncResult result)
{
try
{
//返回值是你收到了多少字节
Socket s = result.AsyncState as Socket;
int num = s.EndReceive(result);
//进行消息处理
Encoding.UTF8.GetString(resultBytes, 0, num);
//异步继续接收消息
s.BeginReceive(resultBytes, 0, resultBytes.Length, SocketFlags.None, ReceiveCallBack, s);
}
catch (SocketException e)
{
print("接收消息处问题" + e.Message + e.ErrorCode);
}
}发送消息
BeginSend
EndSend
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
byte[] bytes = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("123123123");
socketTcp.BeginSend(bytes, 0, bytes.Length, SocketFlags.None, (result) =>
{
try
{
socketTcp.EndSend(result);
print("发送成功");
}
catch (SocketException e)
{
print("发送错误" + e.Message + e.ErrorCode);
throw;
}
}, socketTcp);
② Socket TCP通信中的异步方法2(Async结尾方法)
关键变量类型
SocketAsyncEventArgs他会作为
Async异步方法的传入值我们需要通过它进行一些关键参数的赋值
成员变量:
- 委托:Completed。
- 参数一:服务端套接字。
- 参数二:
SocketAsyncEventArgs类成员实例。- 获取连入的客户端:AcceptSocket。
- 获取当前Socket状态:SocketError。
- 接和发字节数组方法:SetBuffer(字节数组,开始位置,发几个)
- 接收数据的数组:Buffer
- 接收数据的大小:BytesTransferred
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
SocketAsyncEventArgs e = new SocketAsyncEventArgs();
//注册回调函数事件
e.Completed += (socket, args) =>
{
//首先判断是否成功
if(args.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
//获取连入的客户端socket
Socket clientSocket = args.AcceptSocket;
(socket as Socket).AcceptAsync(args);
}
else
{
print("连入客户端失败" + args.SocketError);
}
};
socketTcp.AcceptAsync(e);
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
//ConnectAsync
SocketAsyncEventArgs e2 = new SocketAsyncEventArgs();
//注册事件
e2.Completed += (socket, args) =>
{
if(args.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
//连接成功
}
else
{
print("连入客户端失败" + args.SocketError);
}
};
socketTcp.ConnectAsync(e2);AcceptAsync(服务端接收客户端)例子同上
ConnectAsync(客户端连入方法)例子同上
服务端和客户端发消息
SendAsync(SocketAsyncEventArgs)
2
3
4
5
SocketAsyncEventArgs e3 = new SocketAsyncEventArgs();
byte[] bytes2 = Encoding.UTF8.GetBytes("12312313");
e3.SetBuffer(bytes2, 0, bytes2.Length);
socketTcp.SendAsync(e3);服务端和客户端接收消息
ReceiveAsync
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
//ReceiveAsync
SocketAsyncEventArgs e4 = new SocketAsyncEventArgs();
byte[] bytes3 = new byte[1024];
//设置接收数据的容器 偏移位置 容量
e4.SetBuffer(bytes3, 0, 1024);
e4.Completed += (socket, args) =>
{
if (args.SocketError == SocketError.Success)
{
print("接收成功");
//处理数据
Encoding.UTF8.GetString(args.Buffer, 0, args.BytesTransferred);
//还想接
args.SetBuffer(0, args.Buffer.Length);
//接受完消息 再接收下一条
(socket as Socket).ReceiveAsync(args);
}
else
{
print("接收失败" + args.SocketError);
//断开连接
}
};
socketTcp.ReceiveAsync(e4);
}
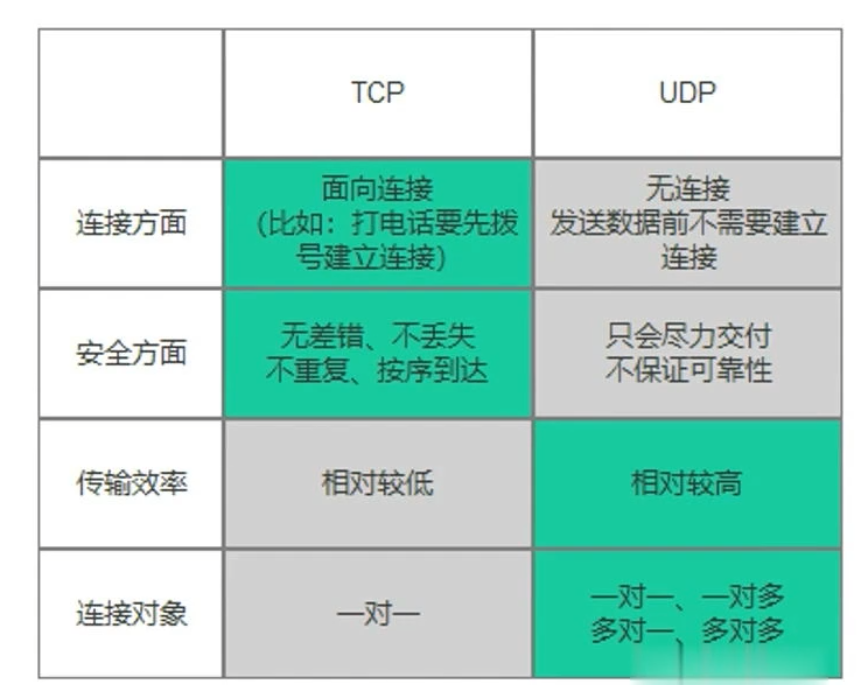
5. UDP通信
(1)通信概述
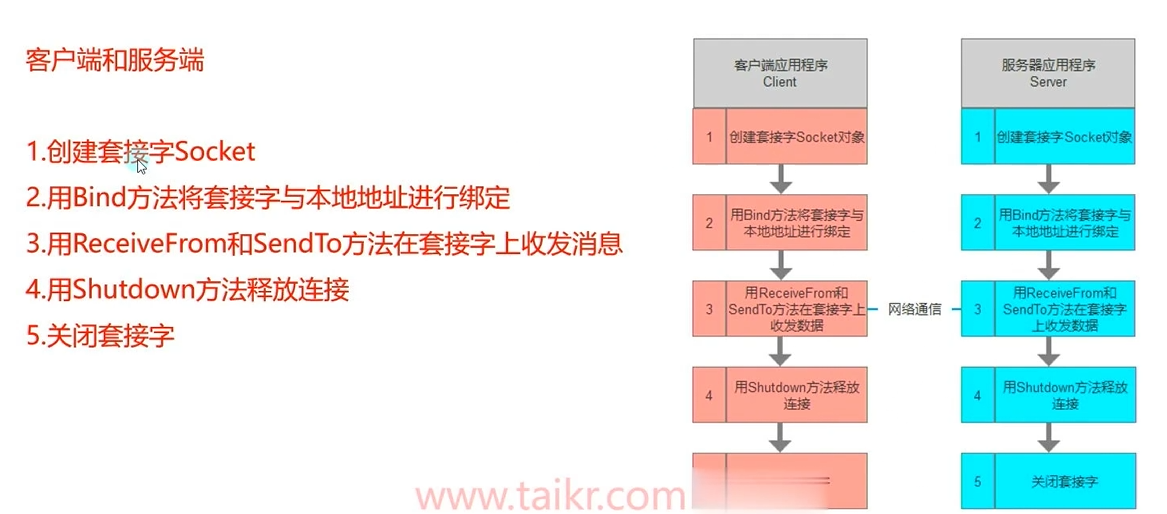
① 相对TCP的区别
② 黏包问题
③ 分包问题
(2) UDP客户端和服务端基础逻辑
- 客户端:
1 | //1.创建套接字 |
- 服务端:
1 | //1.创建套接字 |
① UDP服务端综合练习

疑问:
UDP是无连接的,我们如何记录连接的客户端??
IP地址和端口号UDP收发消息都是通过一个Socket来处理的,我们应该如何处理收发消息?
就是在一个socket进行处理,通过新开线程配合死循环来不停的收消息,有人发我们就给他记录下来。如果不使用心跳信息,我们如何记录上次收到消息的时间??
每一个客户端处理消息时记录一次消息,然后在服务端定时检测,然后清除掉线客户端。
- 代码:
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
{
public IPEndPoint remoteIpPoint;
public string clientStrID;
/// <summary>
/// 上一次收到心跳信息的时间
/// </summary>
public long frontTime = -1;
/// <summary>
/// 心跳消息时间间隔
/// </summary>
private static int TIME_OUT_TIME = 10;
public ClientSocket(string ip, int port)
{
//规则和外面一样
clientStrID = ip + port;
remoteIpPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(ip), port);
}
public void Receive(byte[] bytes)
{
//处理消息和接收消息 用不同的容器 避免出现问题
byte[] cacheBytes = new byte[1024];
bytes.CopyTo(cacheBytes, 0);
//收到信息 记录时间 单位为秒
frontTime = DateTime.Now.Ticks / TimeSpan.TicksPerSecond;
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(MsgHandle, cacheBytes);
}
private void MsgHandle(Object obj)
{
//如果有人恶意发送垃圾消息,这里会报错 所以加try catch
//正常要先建立一层Tcp连接 再去发UDP消息
//如果服务端这边有连接 才会去处理消息。
try
{
byte[] bytes = obj as byte[];
int nowIndex = 0;
//先处理ID
int msgID = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes, nowIndex);
nowIndex += 4;
//再处理长度
int msgLength = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes, nowIndex);
nowIndex += 4;
//再解析消息体
switch (msgID)
{
case 1001:
PlayerMsg playerMsg = new PlayerMsg();
playerMsg.Reading(bytes, nowIndex);
Console.WriteLine("角色姓名:{0}", playerMsg.playerData.name);
Console.WriteLine("角色ID:{0}", playerMsg.playerID);
Console.WriteLine("角色等级:{0}", playerMsg.playerData.lev);
break;
case 1003:
//处理退出
Program.serverSocket.RemoveClient(clientStrID);
break;
}
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("处理消息时出错" + e.Message);
//出错就不用记录了
Program.serverSocket.RemoveClient(clientStrID);
}
}
public void Close()
{
remoteIpPoint = null;
}
}
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
{
private Socket socket;
public Dictionary<string, ClientSocket> clientDic = new Dictionary<string, ClientSocket>();
private bool isClose;
/// <summary>
/// 开启服务器
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ip">ip地址</param>
/// <param name="port">端口号</param>
public void Start(string ip, int port)
{
socket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Dgram, ProtocolType.Udp);
//绑定本机地址
IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(ip), port);
try
{
socket.Bind(ipPoint);
isClose = false;
Console.WriteLine("服务器开启,等待客户端连接");
//消息接收的处理
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(ReceiveMsg);
//定时检测超时限制
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(CheckTimeOut);
}
catch (SocketException e)
{
Console.WriteLine(e.Message + e.ErrorCode);
}
}
private void CheckTimeOut(object obj)
{
long nowTime = 0;
List<string> clients = new List<string>();
while (true)
{
//每30秒检测一次 是否移除尝试价没有接收到消息的客户端
Thread.Sleep(30000);
nowTime = DateTime.Now.Ticks / TimeSpan.TicksPerSecond;
foreach (ClientSocket socket in clientDic.Values)
{
//foreach不能直接移除字典里的东西
if (nowTime - socket.frontTime >= 10)
{
//放到待删除列表中
clients.Add(socket.clientStrID);
}
}
//从待删除的列表中 移除超时的客户端
for (int i = 0; i < clients.Count; i++)
{
RemoveClient(clients[i]);
}
clients.Clear();
}
}
//接收即连入,只要接收消息,就把人连入,连入之后就不再记录
private void ReceiveMsg(object obj)
{
EndPoint remoteIpPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Any, 0);
byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
string strID = "";
string ip;
int port;
while (!isClose)
{
if (socket.Available > 0)
{
lock (socket)
{
socket.ReceiveFrom(bytes, ref remoteIpPoint);
}
ip = (remoteIpPoint as IPEndPoint).Address.ToString();
port = (remoteIpPoint as IPEndPoint).Port;
strID = ip + port.ToString();
if (!clientDic.ContainsKey(strID))
{
//收到消息时 我们可以判断 是不是记录了这个客户端的信息
ClientSocket clientSocket = new ClientSocket(ip, port);
clientDic.Add(strID, clientSocket);
Console.WriteLine(ip + "已经连入....");
clientDic[strID].Receive(bytes);
}
else
{
//如果记录了 直接用字典里面的
clientDic[strID].Receive(bytes);
}
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 发送消息
/// </summary>
/// <param name="msg">发送信息对象</param>
/// <param name="ipPoint">端口和ip地址对象</param>
public void SendTo(BaseMsg msg, IPEndPoint ipPoint)
{
try
{
lock (socket)
{
socket.SendTo(msg.Writing(), ipPoint);
Console.WriteLine("发送成功");
}
}
catch (SocketException e)
{
Console.WriteLine("发送失败" + e.Message + e.ErrorCode);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
Console.WriteLine("发送消息出现问题(可能是序列化的问题)" + e.Message);
}
}
public void Close()
{
if (socket != null)
{
isClose = true;
socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
socket.Close();
socket = null;
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 广播
/// </summary>
/// <param name="msg"></param>
public void Broadcast(BaseMsg msg)
{
foreach (ClientSocket item in clientDic.Values)
{
SendTo(msg, item.remoteIpPoint);
}
}
public void RemoveClient(string clientID)
{
if (clientDic.ContainsKey(clientID))
{
Console.WriteLine("客户端{0}已断开", clientID);
clientDic.Remove(clientID);
}
}
}
② UDP客户端综合练习

2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
37
38
39
40
41
42
43
44
45
46
47
48
49
50
51
52
53
54
55
56
57
58
59
60
61
62
63
64
65
66
67
68
69
70
71
72
73
74
75
76
77
78
79
80
81
82
83
84
85
86
87
88
89
90
91
92
93
94
95
96
97
98
99
100
101
102
103
104
105
106
107
108
109
110
111
112
113
114
115
116
117
118
119
120
121
122
123
124
125
126
127
128
129
130
131
132
133
134
135
136
137
138
139
140
141
142
143
144
145
146
147
148
149
150
151
152
153
154
155
156
157
158
159
160
161
162
163
164
165
166
167
168
169
170
171
172
173
174
175
176
177
178
179
180
181
182
183
184
185
186
187
188
{
public static UdpNetMgr Instance => instance;
private static UdpNetMgr instance;
public Socket socket;
private byte[] bytes = new byte[1024];
private int nowIndex;
private bool isClose = true;
EndPoint serverIpPoint;
//两个队列容器
//接收和发送消息的队列 在多线程里面可以操作
Queue<BaseData> sendQueue = new Queue<BaseData>();
Queue<BaseData> receiveQueue = new Queue<BaseData>();
private BaseData baseData;
private void Awake()
{
instance = this;
DontDestroyOnLoad(this.gameObject);
}
/// <summary>
/// 建立UDP网络通信
/// </summary>
/// <param name="ip">远端IP地址</param>
/// <param name="port">端口号</param>
public void StartClient(string ip, int port)
{
//当前是开启状态 就不要再开了
if (!isClose)
return;
//记录下来
serverIpPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse(ip), port);
IPEndPoint ipPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Parse("127.0.0.1"), 8081);
try
{
socket = new Socket(AddressFamily.InterNetwork, SocketType.Dgram, ProtocolType.Udp);
socket.Bind(ipPoint);
print("客户端已经启动");
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(ReceiveMsg);
ThreadPool.QueueUserWorkItem(SendMsg);
}
catch (Exception e)
{
print("启动Socket出现问题" + e.Message);
}
isClose = false;
}
private void ReceiveMsg(object obj)
{
EndPoint tempIpPoint = new IPEndPoint(IPAddress.Any, 0);
while (!isClose)
{
if (socket.Available > 0 && socket != null)
{
try
{
socket.ReceiveFrom(bytes, ref tempIpPoint);
//为了避免处理 非服务器发来的 骚扰消息
if (!tempIpPoint.Equals(serverIpPoint))
{
//有非服务器发来的消息,跳过不处理
continue;
}
nowIndex = 0;
//先处理ID
int msgID = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes, nowIndex);
nowIndex += 4;
//再处理长度
int msgLength = BitConverter.ToInt32(bytes, nowIndex);
nowIndex += 4;
//处理消息体
BaseMsg msg = null;
switch (msgID)
{
case 1001:
msg = new PlayerMsg();
msg.Reading(bytes, nowIndex);
break;
}
if (msg != null)
{
receiveQueue.Enqueue(msg);
}
}
catch (SocketException e)
{
print("数据接收错误" + e.Message + e.ErrorCode);
}
catch (Exception a)
{
print("数据接收错误(非网络错误)" + a.Message);
}
}
}
}
private void SendMsg(object obj)
{
while (!isClose)
{
if (sendQueue.Count > 0 && socket != null)
{
try
{
socket.SendTo(sendQueue.Dequeue().Writing(), serverIpPoint);
}
catch (SocketException e)
{
print("发送失败" + e.Message + e.ErrorCode);
}
}
}
}
/// <summary>
/// 发送消息
/// </summary>
/// <param name="msg">消息对象</param>
public void Send(BaseData msg)
{
sendQueue.Enqueue(msg);
}
public void Close()
{
if (socket != null)
{
isClose = true;
QuitMsg msg = new QuitMsg();
//发送一个退出消息给服务器让其移除
socket.SendTo(msg.Writing(), serverIpPoint);
socket.Shutdown(SocketShutdown.Both);
socket.Close();
socket = null;
}
}
void Start()
{
}
// Update is called once per frame
void Update()
{
if (receiveQueue.Count > 0)
{
baseData = receiveQueue.Dequeue();
switch (baseData)
{
case PlayerMsg msg:
print("玩家ID:" + msg.playerID);
print("玩家昵称:" + msg.playerData.name);
print("玩家攻击:" + msg.playerData.atk);
print("玩家等级:" + msg.playerData.lev);
break;
}
}
}
private void OnDestroy()
{
Close();
}C
}