高频算法三十讲
一、反转链表
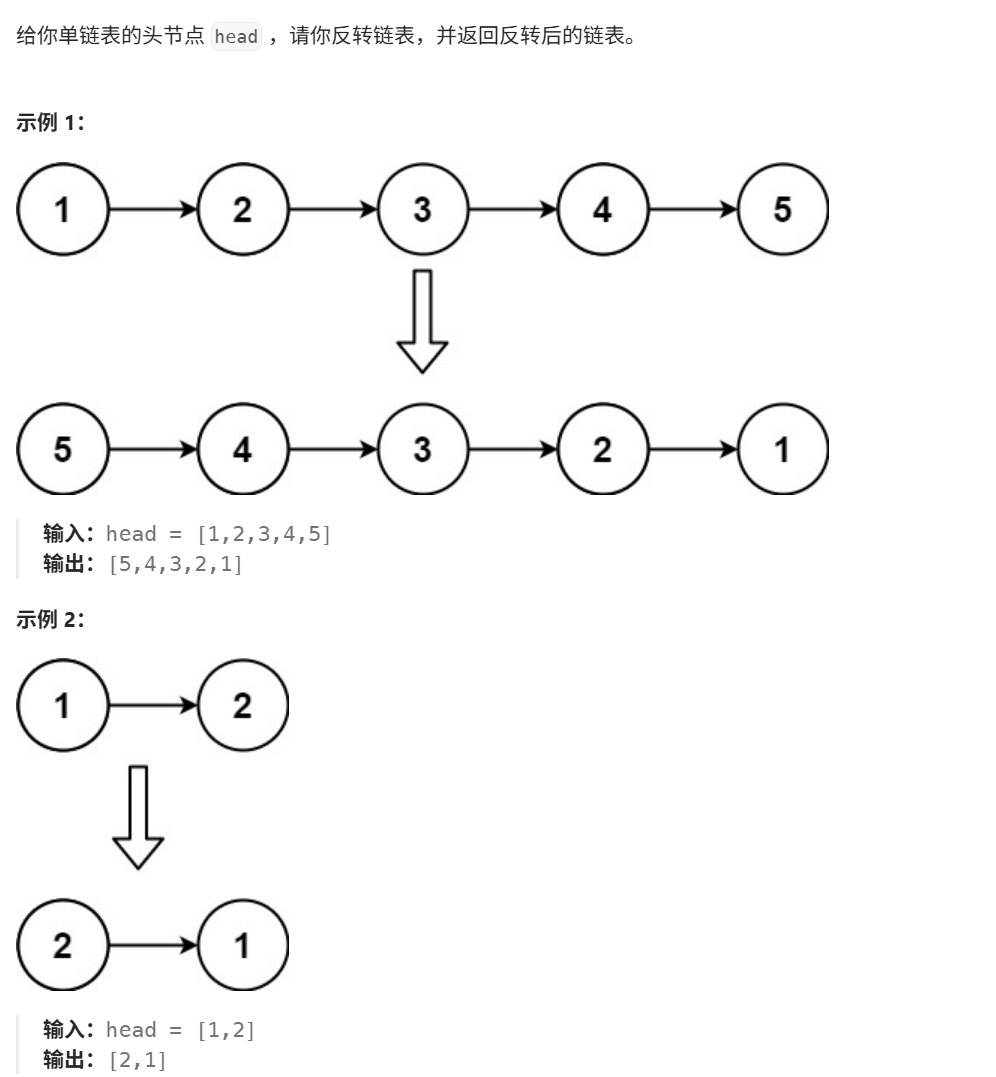
思路:定义三个节点指针,cur,tmp,pre。断后,连前,移节点。
cur:指向头节点
tmp:指向头节点的下一节点
pre:方向节点
以cur断开原本next,从而指向pre方向,再向前移动pr和cur实现方向反转。
tmp=cur->next;
tmp始终都在cur后面,以方便后面cur移动节点
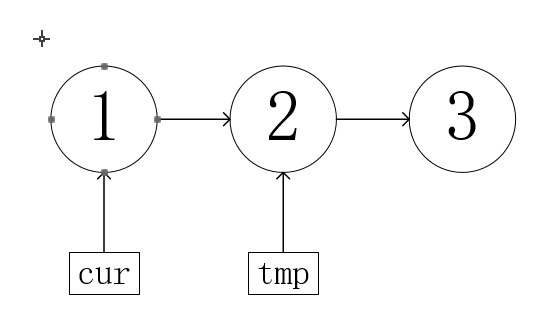
cur->next=pre;
改变链表方向
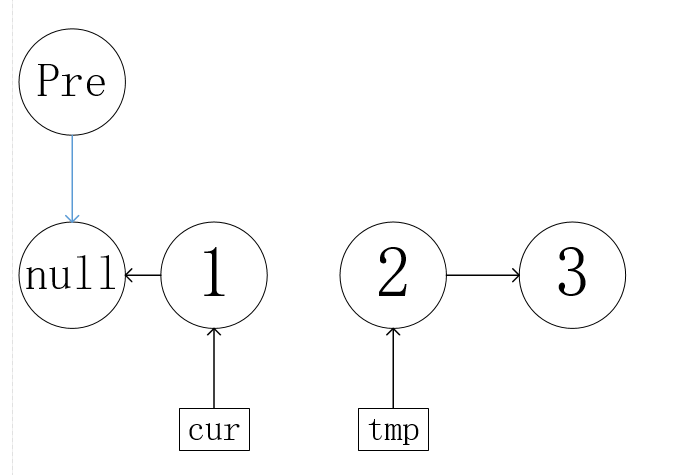
pre=cur; cur=tmp;
节点移动
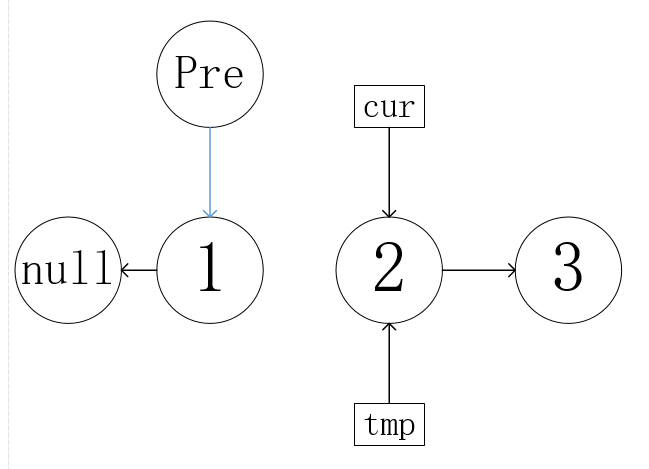
- while循环遍历直到cur为null。
二、轮转数组

1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
| class Solution {
public:
void rotate(vector<int>& nums, int k) {
int n=nums.size();
vector<int> numArry(n);
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
numArry[(i+k)%n]=nums[i];
}
nums.assign(numArry.begin(),numArry.end());
}
};
|
关键公式:(i+k)%n 轮转后索引=(当前索引+轮转步数)%数组大小
三、两数之和

思路:哈希表,遍历数组,用target减去遍历的值去找哈希表。在就返回不在就入表
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution {
public:
vector<int> twoSum(vector<int>& nums, int target) {
unordered_map<int,int> hashtable;
for(int i=0;i<nums.size();i++)
{
auto it=hashtable.find(target - nums[i]);
if(it!=hashtable.end())
{
return {it->second,i};
}
hashtable[nums[i]] =i ;
}
return {};
}
};
|
四、有效的括号

思路:用字典来判断匹配括号,用进出栈的顺序来判断是否为对应括号。如果栈顶元素和字典对应元素相等为匹配成功
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
| class Solution {
public:
bool isValid(string s) {
if(s.size()%2!=0){
return false;
}
unordered_map<char,char> dic={
{')','('},
{'}','{'},
{']','['}
};
stack<char> stk;
for(char ch:s)
{
if(dic.count(ch))
{
if(stk.empty()||stk.top()!=dic[ch])
{
return false;
}
else
{
stk.pop();
}
}
else
{
stk.push(ch);
}
}
return stk.empty();
}
};
|
五、每日温度

思路:单调栈
1.什么是单调栈
单调栈是一个有序的栈,可能从栈顶到栈底单调递增(单调递增栈),也有可能从栈顶到栈底单调递减(单调递减栈)。
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
| stack<int> st;
//此处一般需要给数组最后添加结束标志符,具体下面例题会有详细讲解
for (遍历这个数组)
{
if (栈空 || 栈顶元素大于等于当前比较元素)
{
入栈;
}
else
{
while (栈不为空 && 栈顶元素小于当前元素)
{
栈顶元素出栈;
更新结果;
}
当前数据入栈;
}
}
|
题解:
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
| class Solution {
public:
vector<int> dailyTemperatures(vector<int>& temperatures) {
int n=temperatures.size();
vector<int> answer(n);
stack<int> s;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++){
while(!s.empty()&&temperatures[i]>temperatures[s.top()])
{
answer[s.top()]=i-s.top();
s.pop();
}
s.push(i);
}
return answer;
}
};
|
六、二叉搜索树中第 K 小的元素
1.前序遍历
1.访问根节点;2.访问当前节点的左子树;3.若当前节点无左子树,则访问当前节点的右子树;即考察到一个节点后,即刻输出该节点的值,并继续遍历其左右子树。(根左右)
因为要在遍历完某个树的根节点的左子树后接着遍历节点的右子树,为了能找到该树的根节点,需要使用栈来进行暂存。中序和后序也都涉及到回溯,所以都需要用到栈。
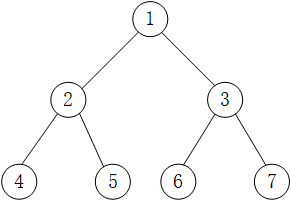
图 中二叉树采用先序遍历得到的序列为:1 2 4 5 3 6 7
2. 中序遍历
二叉树中序遍历的实现思想是:1.访问当前节点的左子树;2.访问根节点;3.访问当前节点的右子树。即考察到一个节点后,将其暂存,遍历完左子树后,再输出该节点的值,然后遍历右子树。(左根右)
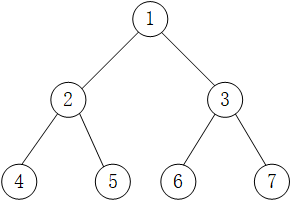
上图中二叉树采用中序遍历得到的序列为:4 2 5 1 6 3 7
3. 后序遍历
二叉树后序遍历的实现思想是:1.访问左子树;2.访问右子树;3.完成该节点的左右子树的访问后,再访问该节点。即考察到一个节点后,将其暂存,遍历完左右子树后,再输出该节点的值。(左右根)
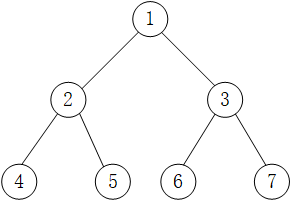
对上图 中二叉树进行后序遍历的结果为:4 5 2 6 7 3 1
4.题目
思路:因为左树都是比节点小,所以优先使中序遍历;
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
|
class Solution {
public:
int kthSmallest(TreeNode* root, int k) {
stack<TreeNode*> stk;
while(root!=nullptr||stk.size()>0){
while(root!=nullptr){
stk.push(root);
root=root->left;
}
root=stk.top();
stk.pop();
k--;
if(k==0)
{
break;
}
else{
root=root->right;
}
}
return root->val;
}
};
|
七、求根节点到叶节点数字之和
1.深度优先遍历
一种用于遍历或搜索树或图的算法。 沿着树的深度遍历树的节点,尽可能深的搜索树的分支。当节点v的所在边都己被探寻过或者在搜寻时结点不满足条件,搜索将回溯到发现节点v的那条边的起始节点。整个进程反复进行直到所有节点都被访问为止。属于盲目搜索,最糟糕的情况算法时间复杂度为O(!n)。
2.题目

思路:遇到树或者图,就想递归处理或者前中后遍历
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
|
class Solution {
public:
int sumNumbers(TreeNode* root) {
return dfs(root,0);
}
int dfs(TreeNode* root,int prenum){
if(root==nullptr)
return 0;
int sum=prenum*10+root->val;
if(root->left==nullptr&&root->right==nullptr)
{
return sum;
}else{
return dfs(root->left,sum)+dfs(root->right,sum);
}
}
};
|
八、